Angioedema and anaphylaxis are serious medical conditions that involve rapid swelling and allergic reactions, respectively. Both can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, and understanding their causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies is critical for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. This article explores these conditions in detail, including their management with medications like ceftriaxone wholesale, where relevant, and provides actionable insights for awareness and preparedness.
Understanding Angioedema
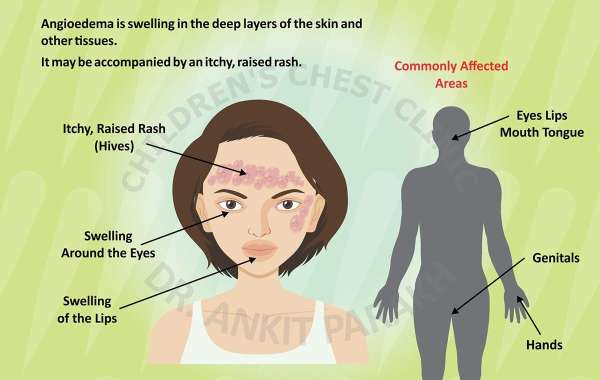
Angioedema is characterized by sudden, localized swelling beneath the skin, often affecting areas like the face, lips, tongue, throat, or extremities. Unlike hives, which affect the skin’s surface, angioedema occurs in deeper tissues, leading to more severe symptoms. It can be triggered by various factors, including allergic reactions, medications, genetic conditions, or infections.
Causes of Angioedema
Allergic Angioedema: Triggered by allergens such as foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish), insect stings, or medications like penicillin or ceftriaxone wholesale (a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in bulk for hospital settings).
Hereditary Angioedema (HAE): A genetic disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of C1 inhibitor protein, leading to recurrent swelling episodes.
Drug-Induced Angioedema: Commonly linked to ACE inhibitors (used for hypertension) or antibiotics like ceftriaxone wholesale, which may be procured in large quantities for treating infections but can occasionally trigger swelling.
Infections or Autoimmune Conditions: Bacterial or viral infections, sometimes treated with ceftriaxone wholesale, may cause angioedema as a secondary reaction.
Symptoms
Symptoms of angioedema include:
Rapid swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Pain or warmth in affected areas.
Difficulty breathing or swallowing if the airway is involved.
Abdominal pain or swelling in severe cases.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause and severity:
Antihistamines: For allergic angioedema, to reduce swelling.
Corticosteroids: To control inflammation.
Epinephrine: For severe cases involving airway compromise.
C1 Inhibitor Replacement: For hereditary angioedema.
Discontinuation of Triggering Medications: If ceftriaxone wholesale or other drugs are implicated, stopping their use is critical.
In healthcare settings, ceftriaxone wholesale is often used to manage infections that might indirectly contribute to angioedema, but its role as a potential trigger must be monitored.
Prevention
Avoid known allergens or triggers.
Genetic testing for those with a family history of HAE.
Careful monitoring when starting new medications, including bulk antibiotics like ceftriaxone wholesale.
Understanding Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, systemic allergic reaction that can involve multiple organ systems and progress rapidly to life-threatening shock. It is typically triggered by an immune response to an allergen, leading to the release of histamine and other chemicals that cause widespread symptoms.
Causes of Anaphylaxis
Food Allergies: Peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, and dairy are common culprits.
Medications: Antibiotics like ceftriaxone wholesale, NSAIDs, or contrast dyes used in medical imaging.
Insect Stings: Bee or wasp venom.
Latex or Other Substances: Exposure in medical or occupational settings.
Ceftriaxone wholesale, while essential for treating severe bacterial infections in hospitals, can rarely cause anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals, necessitating careful patient screening.
Symptoms
Anaphylaxis symptoms typically appear within minutes of exposure and include:
Skin reactions: Hives, itching, or flushing.
Respiratory distress: Wheezing, shortness of breath, or throat swelling.
Cardiovascular symptoms: Rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, or fainting.
Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
Treatment
Immediate intervention is critical:
Epinephrine: Administered via auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) to reverse symptoms.
Antihistamines and Corticosteroids: To manage residual symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Oxygen and IV Fluids: For severe cases requiring hospitalization.
Monitoring: Patients receiving ceftriaxone wholesale in hospitals should be observed for allergic reactions.
Prevention
Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if at risk.
Wear medical alert bracelets identifying allergies.
Avoid known triggers, including medications like ceftriaxone wholesale if a prior reaction has occurred.
Educate family and coworkers about emergency response.
Key Differences Between Angioedema and Anaphylaxis
While angioedema and anaphylaxis can overlap, they differ in scope:
Angioedema: Primarily involves localized swelling, though it can affect the airway and mimic anaphylaxis.
Anaphylaxis: A systemic reaction affecting multiple systems (skin, lungs, heart, etc.), often including angioedema as a symptom.
For example, a patient receiving ceftriaxone wholesale for a bacterial infection might develop angioedema (swelling of the face) or progress to anaphylaxis (swelling plus difficulty breathing and low blood pressure). Recognizing these distinctions guides treatment.
Role of Ceftriaxone in Treatment and Risk
Ceftriaxone wholesale is a cephalosporin antibiotic widely used in hospitals for infections like pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis. Its bulk availability ensures cost-effective treatment in large-scale settings. However, as with any medication, it carries risks:
Allergic Reactions: Rarely, ceftriaxone wholesale can trigger angioedema or anaphylaxis, particularly in patients with a history of penicillin or cephalosporin allergies.
Management: If a reaction occurs, discontinue ceftriaxone wholesale, administer epinephrine, and switch to an alternative antibiotic (e.g., vancomycin).
Screening: Hospitals using ceftriaxone wholesale should screen patients for drug allergies before administration.
Healthcare providers must balance the benefits of ceftriaxone wholesale in treating infections against its potential to cause allergic reactions, ensuring rapid response protocols are in place.
Emergency Preparedness
Both conditions require swift action:
Know the Signs: Swelling, breathing difficulty, or systemic symptoms demand immediate attention.
Access to Epinephrine: Essential for at-risk individuals.
Medical Follow-Up: After an episode, consult an allergist to identify triggers and adjust treatment plans, including avoiding ceftriaxone wholesale if implicated.
Long-Term Management
Allergy Testing: To pinpoint triggers, including medications like ceftriaxone wholesale.
Education: Patients and families should understand symptoms and emergency protocols.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoid allergens and carry emergency medications.
Conclusion
Angioedema and anaphylaxis are medical emergencies that require prompt recognition and treatment. Angioedema involves localized swelling, while anaphylaxis is a systemic allergic reaction, but both can be triggered by allergens, medications like ceftriaxone wholesale, or other factors. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatments empowers individuals to act quickly and prevent complications. In healthcare settings, ceftriaxone wholesale is a valuable tool for infection management but must be used cautiously due to its potential to cause allergic reactions. By staying informed and prepared, patients and providers can minimize risks and ensure safety.