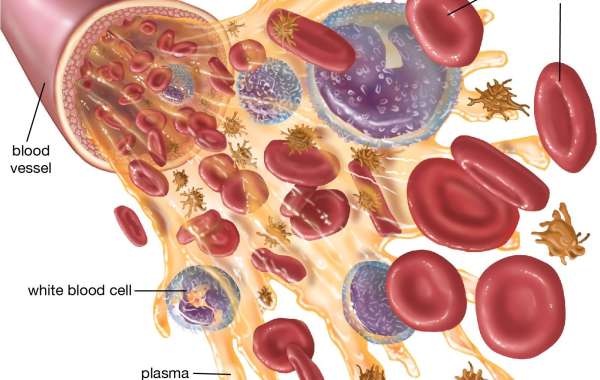
White blood cells (WBCs), also known as leukocytes, play a critical role in the immune system by defending the body against infections, foreign invaders, and abnormal cell growth. When the white blood cell count in the body rises above the normal range, it can indicate a variety of physiological and pathological conditions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes of elevated white blood cells, what they mean for your health, and when it may signal the need for medical treatment. This information is especially relevant for healthcare providers, pharmacists, and even ceftriaxone injection wholesalers who deal with medical supplies for infection control.
What Is Considered a High White Blood Cell Count?
A normal white blood cell count typically ranges from 4,000 to 11,000 cells per microliter of blood. A count above this range is known as leukocytosis. The significance of a high white blood cell count depends on the individual’s overall health, symptoms, and other diagnostic results.
Types of White Blood Cells
To understand elevated WBC levels, it’s helpful to know that there are five main types of white blood cells:
Neutrophils Fight bacterial infections
Lymphocytes Combat viral infections and help in immune response
Monocytes Remove dead or damaged tissue
Eosinophils Respond to allergens and parasites
Basophils Play a role in allergic responses
A rise in a specific type of white blood cell can provide clues to the underlying cause of leukocytosis.
Common Causes of High White Blood Cell Counts
1. Infections
The most common cause of elevated white blood cells is infection. Whether bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic, infections trigger an immune response that includes the production of more WBCs.
Bacterial infections (e.g., pneumonia, sepsis): Often increase neutrophils
Viral infections (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus): Usually raise lymphocytes
Parasitic infections (e.g., malaria): Elevate eosinophils
In cases of severe infections like bacterial meningitis or sepsis, potent antibiotics like ceftriaxone are used. Ceftriaxone injection wholesalers play a crucial role in ensuring that hospitals and clinics maintain an adequate stock of this life-saving antibiotic.
2. Inflammatory Conditions
Chronic inflammation can also lead to increased WBC levels. Conditions such as:
Rheumatoid arthritis
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Lupus
trigger the immune system, often resulting in a sustained elevation in WBC count.
3. Stress and Physical Trauma
Physical or emotional stress, surgery, trauma, or even intense exercise can temporarily raise white blood cell counts. This is the body’s way of preparing to fight potential infections or recover from injury.
4. Allergic Reactions
Allergies to foods, medications, or environmental substances can cause an increase in eosinophils. In severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis, WBC counts can surge dramatically.
5. Medications
Certain medications may cause leukocytosis as a side effect. These include:
Corticosteroids
Lithium
Epinephrine
Even antibiotics like ceftriaxone may influence WBC counts as they interact with infections in the body. Understanding drug interactions is essential for both healthcare providers and ceftriaxone injection wholesalers when advising clients and managing inventory.
6. Bone Marrow Disorders
Some forms of cancer, such as leukemia, originate in the bone marrow and lead to uncontrolled production of white blood cells. In these cases, WBC counts can be extremely high, but the cells are often immature or non-functional.
7. Immune System Disorders
Autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies can affect WBC levels, sometimes causing them to rise as the body attempts to compensate for dysfunctional immunity.
Symptoms Associated with High White Blood Cells
An elevated WBC count is often discovered through a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test ordered for other symptoms. Depending on the cause, a person may experience:
Fever or chills
Fatigue
Body aches
Inflammation or redness
Unexplained weight loss
Night sweats
Pain or discomfort in a localized area (e.g., chest, abdomen)
Diagnosing the Underlying Cause
If your white blood cell count is high, your healthcare provider may order additional tests to determine the cause:
Differential WBC count (to identify which type of WBC is elevated)
Blood cultures (to identify infections)
Imaging tests (such as X-rays or CT scans for internal infections)
Bone marrow biopsy (if leukemia or other marrow issues are suspected)
Treatment Options for Elevated WBCs
The treatment for a high white blood cell count depends entirely on the underlying cause.
1. Antibiotics for Infections
For bacterial infections, broad-spectrum antibiotics like ceftriaxone are often used. Ceftriaxone is particularly effective for treating serious infections such as
Meningitis
Urinary tract infections
Septicemia
Because of its importance in treating life-threatening infections, the role of ceftriaxone injection wholesalers is crucial in ensuring timely and reliable distribution to healthcare facilities.
2. Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Drugs
For autoimmune or inflammatory disorders, drugs like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may help reduce white blood cell counts and inflammation.
3. Cancer Treatment
In cases where leukemia or another malignancy is responsible, treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation, or bone marrow transplantation.
4. Supportive Care
For temporary elevations due to stress or trauma, no treatment may be necessary aside from rest and supportive care.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
If you’ve had a high white blood cell count, your doctor will likely want to monitor your levels over time. Repeating the CBC test can help track progress, assess response to treatment, or catch recurrence of disease.
For hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic labs, having access to reliable medication supplies is a part of this monitoring process. This is why sourcing from a dependable ceftriaxone injection wholesaler is essential for consistent treatment outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience:
Persistent fever
Night sweats
Swollen lymph nodes
Unexplained fatigue or weight loss
Bleeding or bruising easily
These may be signs of a serious condition requiring immediate evaluation.
Final Thoughts
A high white blood cell count is a significant marker of immune system activity and can indicate anything from a mild infection to a serious illness like leukemia. Understanding what causes leukocytosis and how it is treated can lead to quicker diagnoses and better health outcomes.
Whether you're a healthcare professional, patient, or part of the medical supply chain, it’s important to recognize the critical role medications like ceftriaxone play in managing infections. Ensuring a steady and safe supply from a trusted ceftriaxone injection wholesaler supports effective care and timely intervention.
If your white blood cell count is high, don't ignore it talk to your doctor, get the appropriate tests, and follow a treatment plan tailored to your needs.